Japan technology briefing for the President of Germany, Horst Köhler
Japan is a technology super power full of creativity and power to innovate
Tokyo, April 3, 2005
Briefing given to the President of Germany, Horst Koehler, and his wife, by Gerhard Fasol in the German Embassy, Tokyo, on April 3, 2005, at the beginning of the President’s official visit to Japan to open the “German Year in Japan”. Accompanying President Horst Koehler were 20-30 leaders of Germany, including Members of Parliament, the President of the German Federation of Industry – the German Ambassador to Japan was chairing the meeting.
1 Excellency, Dear President: Japan is a technology super power
Japan is a technology super power, with strong creativity and power to innovate. I would like to illustrate this fact with a few examples, how innovation in Japan creates new industry sectors and new employment, I would like to describe some consequences for Germany and for Europe, and express some recommendations.
- Many inventions, which change the world and which create employment, come from Japan. I would like mention two examples here:
- Gallium-Nitride light emitting diodes replace light bulbs and fluorescent tubes for illumination and displays
- The mobile internet changes our life, started in Japan and it’s development is most advanced in Japan
- There are many more technology breakthroughs and inventions from Japan, for example carbon nano-tubes or electronic money
- Interaction with Japan enforced total restructuring of leading US companies, including INTEL and MOTOROLA. According to my knowledge, there are almost no European companies yet which were forced to totally restructure their business due to interaction with Japan. I feel that this may happen in the future.
- Was does this mean for Germany and Europe?
- In Japan, as everywhere else, innovation is driven by individual ‘heroes’— not by industry associations or government: Europe should even more than today empoyer individuals
- One way to empower creative European ‘heroes’ is for Europe to introduce as quickly as possible a single, cheap and efficient European Patent
- Technology cooperation is not an aim in itself, but it should achieve well defined and measurable targets
2 Gallium-Nitride light emitting diodes (blue LEDs) are changing the illumination industry and our lives
Thomas Alva Edison invented light bulbs in 1879 (US Patent No. 223, 898). Glass tubes in radio and television receivers have been replaced a long time ago by semiconductors. Semiconductors use far less energy, have a longer operational lifetime, and are much more friendly to the environment.
About 15 years ago, Shuji Nakamura invented the technologies[1] to replace light bulbs and fluorescent tubes by semiconductors, in same way as this has happened in radios and television receivers a long time ago. Shuji Nakamura invented these technology in a small company, Nichia Kagaku Kougiyou, located in Anan, about two hours by airplane from Tokyo. He achieved these breakthrough inventions essentially on his own and with great personal sacrifice.
3 Japan is pioneering the mobile internet
- Today the mobile internet is a major component of the economy of Japan
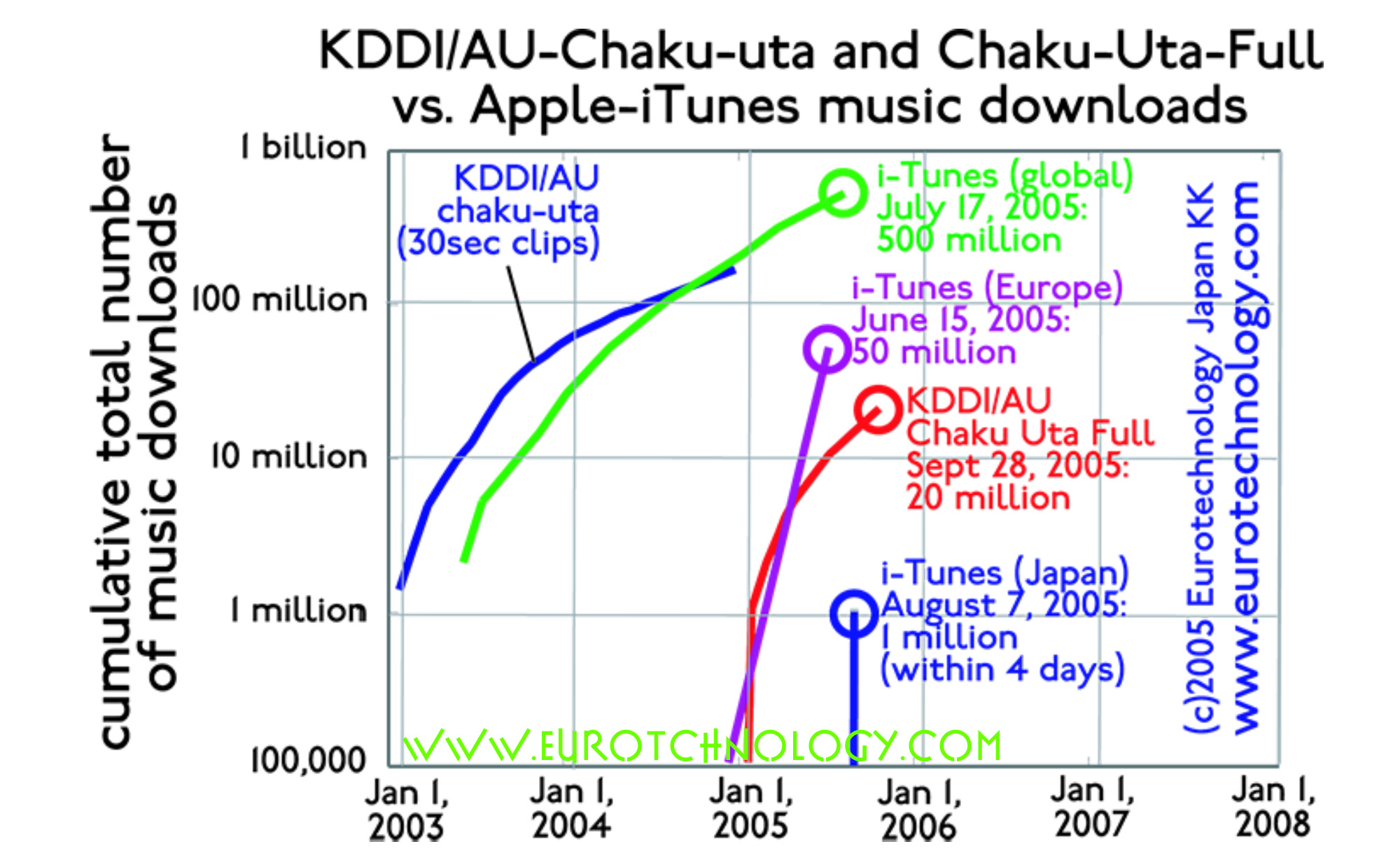
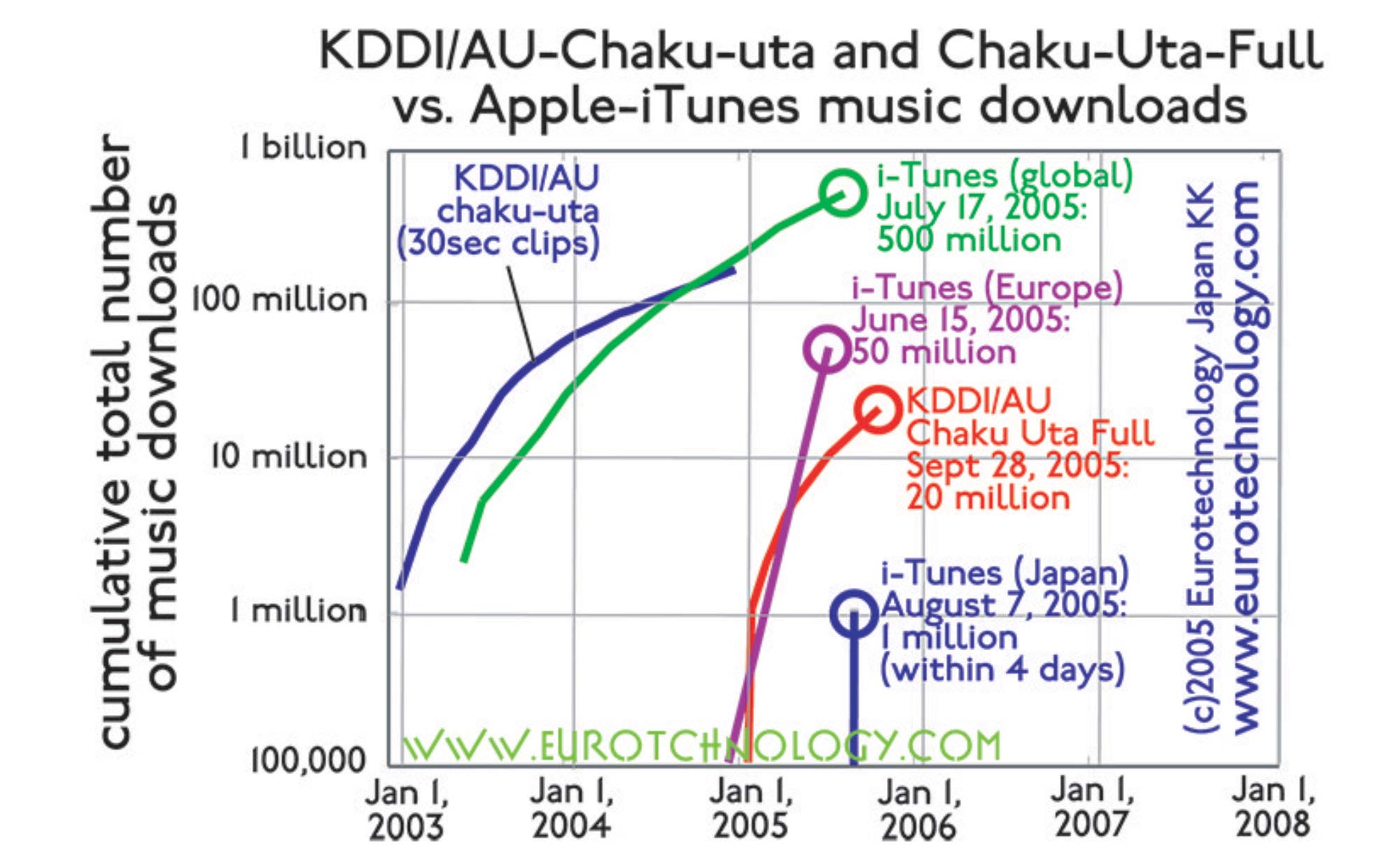
- While “third generation” (3G, UMTS) mobile communication systems with 384 kbps data transfer rates is being introduced this year in Europe after many delays, mobile internet deployed nationwide in Japan since 2003 by the Japanese company KDDI already has six times higher speed (2.4 Mbps = 2400 kbps) since several years ago. This higher speed enables for example the transmission of full music works, which is not yet practical in Europe, and contributes to the development of new industries in Japan, which cannot yet thrive in Europe, because the infrastructure is not yet in place in Europe.
- Mobile music is revolutionizing the music industry. Already today about 20% of music sales is via the mobile internet.
- Mobile books revolutionize our literary culture. During January 2005 alone, KDDI/AU (Japan’s second largest mobile operator) sold 50,000 electronic books on the mobile internet.
- Why was the mobile internet developed in Japan and not in Europe? A determining factor is research and development: NTT does considerably more research and development than European telecommunications companies. Therefore, already in 1997, Japan had a national packet switched mobile data network, many years before Europe introduced GPRS (Europe’s first version of a packet switched mobile data network).
- Japan’s mobile internet was enabled by a small number of heroic pioneers: I would like to emphasize the work by a Japanese woman—Matsunaga Mari. The mobile internet in Europe also owes much to her genius.
4 Interaction with Japan changes technology industries
Japan’s technology industries some years ago caused US electronics companies including INTEL and MOTOROLA to restructure totally. Could the German automobile industry expect similar interactions with Japan?
What is the significance for Germany? Technologies and business models are globally valid. Therefore Japanese innovations, such as light emitting diodes or mobile phones unavoidably reach Germany. Interaction with Japan have forced leading US corporations including INTEL and MOTOROLA to totally restructure: INTEL switched it’s entire business from memory chips to CPUs because of Japanese competition. With increasing interaction between Japan and Germany, I expect similar impact by Japan on Germany in the future.
As an example, I would like to mention the automobile industry sector. Toyota’s market capitalization is US$ 122 Billion, while DaimlerChrysler’s is around US$ 45 Billion, almost three times smaller. It is therefore obvious that Toyota by increasing business activities in Europe, can have major impact on the largest European car companies. Similar factor three ratios exist between the valuations of Honda and Volkswagen, Nissan and BMW: Honda as well as Nissan enjoy about three times higher valuations by the international investment community than Volkswagen and BMW. I recommend therefore European companies not to neglect Japan.
As an example, we are at present preparing project work with a US company, which will invest about US$ 2 Billion globally this year in new production—100% of this high-technology production investment will be in Japan.
5 Empower individual inventors and engineers: The European Patent
Researchers and companies in Japan and the USA have a great home advantage compared to European researchers and companies, because Japan and the USA have a simple and cost efficient patent system. The table below, taken from an official EU-Website[2] shows that obtaining patent protection for Europe is much more complicated and much more expensive than for USA and Japan. In actual fact, the real situation is even more dramatic than the official table from the EU website shows: in real life, US patents are obtained much cheaper than shown in this table, and obtaining patent coverage for all European countries is much more expensive than the case of 8 countries shown in the table, which only gives protection in a minority of European countries.
A cost efficient and simple European Patent is necessary to correct this European home-disadvantage
6 Why technology cooperation?
An eminent US committee of experts some time ago examined technology cooperation with Japan and optimization with respect to US interests. This committee concluded that technology cooperation is not an aim in itself, but there should be measurable targets. The committee found that a suitable target is the creation of highly paid employment in the USA.
I would recommend, that in case increased technology cooperation with Japan is discussed during the German Year in Japan, that in the same way as the USA did, also Germany examines technology cooperation with Japan overall, and orients technology cooperation towards measurable targets. I can well imagine that creation of highly paid employment in Germany could also be a good way to measure the value of individual cooperation projects.
7 My recommendations for Germany and Europe:
- In Japan as anywhere else, innovation and break throughs are driven by single individuals, not by institutions or government authorities. Therefore: empower individual researchers and developers and engineers
- A user friendly, quick, simple and cost efficient European Patent should be introduced to remove Europe’s handicap for research and innovation compared to US and Japan
- For many German companies the best strategy is not China or Japan, but: China and Japan
- For many US companies Japan is the largest and most important foreign market. For a long time, Japan has been neglected in Germany. Business with Japan creates jobs in Germany.
- Technology cooperation with Japan is not an aim in itself. There must be a measurable target. An eminent US committee examined this question, and reached the conclusion that technology cooperation with Japan should create highly paid employment in the USA. I recommend that German technology cooperation with Japan should also be targeted to achieve a desirable target, such as the creation of highly paid employment in Germany.
Japan technology – References
- Shuji Nakamura, Gerhard Fasol, Stephen J. Pearton, ‘The Blue Laser Diode: The Complete Story’, Springer Verlag (Heidelberg, 2nd Edition, October 2, 2000), ISBN: 3540665056
- http://europa.eu.int/comm/internal−market/en/indprop/patent/2k-41.htm
- Gerhard Fasol, ‘New Opportunities versus old Mistakes: foreign companies in Japan’s high-tech world’, presentation at Stanford University, (Oct 28, 1999)
Copyright notice: photograph of the The President of Germany Horst Köhler is public domain, see Wikipedia here.
Download Gerhard Fasol’s presentation to German President Horst Koehler
If you need the German original or the English translation of Gerhard Fasol’s presentation to German President Horst Koehler please contact us
Copyright 1996-2019 Eurotechnology Japan KK All Rights Reserved