Tag: solar
-
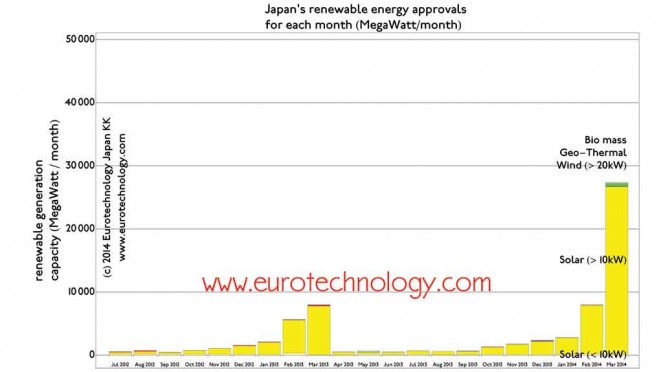
Solar Japan: Japan approves a full Germany worth of renewable energy in a single month
Solar Japan: some of the world’s most attractive feed-in-tariffs In the single month of March 2014 Japan approved almost as much renewable energy projects as all solar ever installed in Germany Japan’s ten regional electricity monopoly operators traditionally kept renewable energy below 1% following an unwritten rule. Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO) kept renewable well…
-
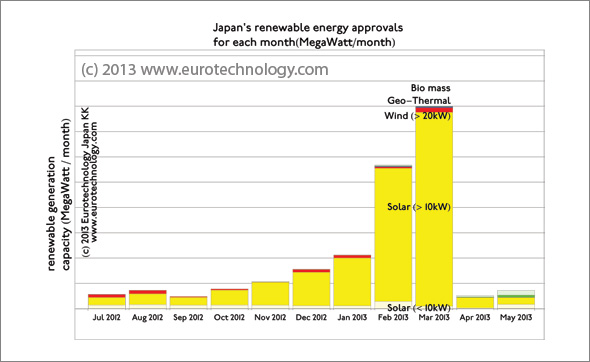
Feed in tariff Japan for renewable energy: approvals drying up?
Feed in tariff Japan for renewable energy are about three times higher than in Germany Approvals peaked just before the latest feed in tariff reduction The figures below show an overview of renewable energy sources currently installed and operational in Japan (the majority of which is water power), and also renewable energy projects approved by…
-

Japan energy – myths versus reality, mantra versus smart
A lecture a the Embassy of Sweden for the Stockholm School of Economics European Institute for Japanese Studies EIJS Outline of the lecture: Thank you to all those who attended the event “Japan’s energy – myths vs reality” at the Embassy of Sweden – an event organized by the European Institute for Japanese Studies of…
-

94% of renewable energy projects approved under Japan’s feed-in-tariff programs are for solar energy generation
Japan’s feed in tariff for renewable energy Almost all projects are for solar energy Feed-in-tariffs for renewable energy where introduced in two stages in Japan. Large scale introduction of feed-in-tariffs (FIT) started with the Law entitled “Special measures concerning renewable energy electric power procurement by operators of electrical utilities law” which came into force on…
-

Japan ought to be heaven for renewable energy (The Economist)
Industry Ministry METI announces renewable energy sources admitted to the feed-in-tariff program Reversing the decline of renewable energy in Japan A few days ago Japan’s industry ministry METI announced the most recent data on renewable energy sources in Japan admitted under the feed-in-tariff (FIT) regulations introduced on July 1, 2012. We have updated our report…
-

Japan to reverse decline of renewable energy – Renewables declined from 25% to 10%
Japan’s renewable energy generation is overwhelmingly water power Japan to reverse decline of renewable energy. The ratio of renewable power generation has decreased from 25% of total electricity generation in 1970 to 10% today. Extremely aggressive feed-in tariffs (FIT) for renewable energy introduced in July 2012 are showing first modest results to reverse this trend…