Japan LNG import costs – we analyze Japan’s official LNG import data
Japan LNG import costs increase 77.5% from 2011-2013
Here we analyze Japan’s liquid natural gas (LNG) costs, which have been driven to record heights – mainly by the very high LNG prices Japan has to pay, and driven even higher by the low YEN exchange rates. If you are interested in precise numerical analysis: you can find detailed graphics and analysis in our Japan-Energy report, based on import data direct from Japan’s Ministry of Finance.
Japan LNG import cost reduction strategies
To reduce Japan’s extremely high payments for energy, Japan’s Government is following several strategies: Japan’s Government seeks to reduce LNG prices by developing new LNG sources, increase coal usage, increase development of renewable energy sources – and work towards restarting nuclear power plants.
Solar projects dominate renewable energy development for now. Our company currently alone is working with a number of clients on a pipeline of about 50 solar projects with a total of approx. 950 MegaWatt – and growing.
If you have questions about Japan’s energy markets – contact us here:
For insights into why Japan’s energy situation has come to where it is today, download the handouts of our talk “Japan’s Energy – Myths vs Reality”, given at the Embassy of Sweden in Tokyo (Alfred Nobel Auditorium) in cooperation with Stockholm School of Economics on June 19.
Liquified gas import costs increased 77.5%

Nuclear power has been replaced largely by electricity produced from imported LNG. Japan’s payments for LNG have dramatically increased. We have analyzed Japan’s official data, and found that the increase is mainly due to increased prices and exchange rate, and much less due to increased volumes.
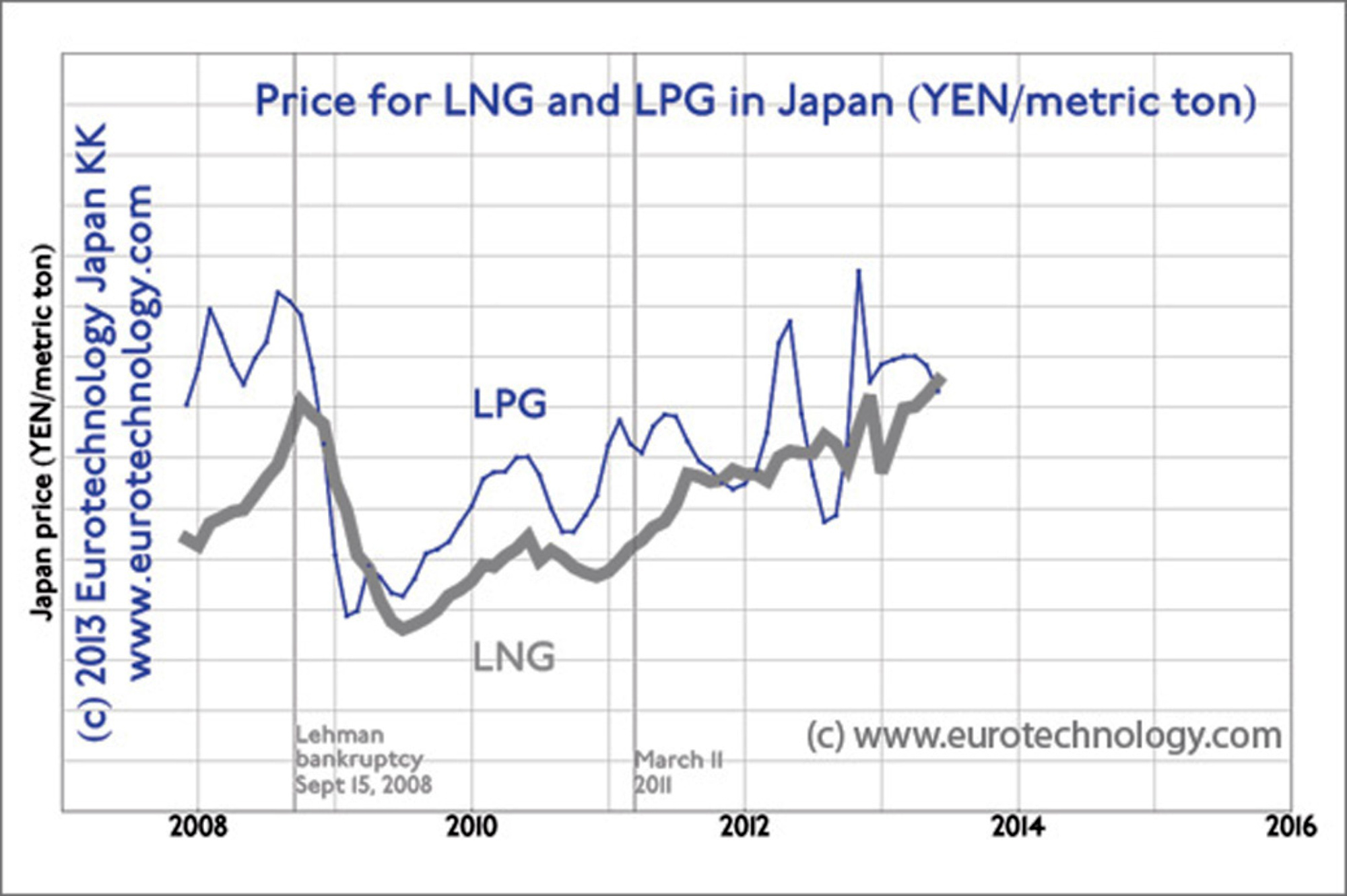
Japan pays higher LNG prices than at the 2008 peak

Japan pays very much higher prices for LNG than Europe or US. The LNG prices Japan pays today are about twice as high as during the slump following the Lehman shock, and are higher than at the peak just before the Lehman bankruptcy in September 2008.
Japan’s liquified gas imports have increased 23%

Due to intensive electricity saving measures, LNG imports have actually increased far less than would be necessary to replace all switched off nuclear power. Today’s LNG import volumes by weight are only about 23% higher then before the March 11, 2011 crisis, while costs are about 77.5% higher.
This shows that Japan’s extremely high payments for LNG imports are much more caused by high prices than by increased import volumes. Therefore Japan’s Governments and private industry strategies to decrease LNG prices for Japan are the way to go for the short term.
Longterm of course, it is necessary to rebuild Japan’s energy architecture, which has been created in 1952 under orders from McArthur’s military Government, and has been essentially frozen in since 1952. Attempts to liberalize Japan’s energy markets, including electricity, have been largely ineffective.
Another approach to liberalization is currently on its way – as described in our detailed report and analysis of Japan’s energy markets
Copyright (c) 2013 Eurotechnology Japan KK All Rights Reserved
Comments and discussions